Satoshi’s wallet: a prime target for quantum attacks
Satoshi’s original Bitcoin wallet, which contained 1.1 million BTC, is being viewed by researchers as a quantum vulnerability. They are assessing how the increasing computing power of computers could impact early Bitcoin addresses.
Satoshi’s Nakamoto estimated bitcoin (1.1 million)BTCThe crypto-world’s ultimate currency is often referred to as. “lost treasure.” The digital ghostship has sat on the blockchain for years without a single onchain transaction. The massive hoard, which is worth between $67 billion and $124 billion according to current market prices, has been a myth.
For a growing group of cryptographers as well as physicists it’s also seen to be a security threat worth billions. This threat does not come from a hacker breaching a server or losing a password. It comes from the advent of an entirely different form of computation. quantum computing.
Quantum machines, as they move from the theoretical labs of research to working prototypes that are powerful enough to be used in real-world applications, pose a threat to cryptographic systems. The encryption used to protect Satoshi’s coins as well as the Bitcoin network, and other parts of global financial infrastructure are all included.
It is not far away “what if.” Race to develop both quantum computers and an quantum-resistant defense This is one of most important and funded technological initiatives of our times. This is the information you need.
Satoshi’s wallets from the early days are easy targets for quantum attacks
Modern Bitcoin wallets usually hide the public keys until there is a transaction. Satoshi’s old pay-topublic-key addresses (P2PK), however, don’t. The public key is permanently displayed onchain.
It is crucial to understand that all Bitcoin addresses do not equal the same thing. Satoshi’s address from 2009 or 2010 is the vulnerability.
Most Bitcoin today is held in pay-to-public-key-hash (P2PKH) addresses, which start with “1,” SegWit addresses that start with “bc1.” The blockchain stores only the hash when coins arrive at these types of addresses. It only shows the real public key after the coins have been spent.
Imagine it as a drop-box at a bank. Anyone who can see the hash of an address is able to drop in money. The metal lock behind the mail slot contains the public key. The lock and its mechanism cannot be seen by anyone. Public key “lock”Your private key is not revealed until you spend your coins. “unlocks” it.
Satoshi’s coin, on the other hand, is stored in P2PK addresses that are much older. This legacy format does not have a hash. This public key is the “lock” in our example. It’s visible and permanent on the blockchain.
It does not make a difference for a traditional computer. Even though it is practically impossible to reverse engineer a public-key to get the private key, this still remains a possibility. A quantum computer can use the public key as a blueprint. This is a clear invitation for anyone to pick up the lock.
Shor’s algorithm allows quantum machines to break Bitcoin
Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm, the security algorithm for Bitcoin (ECDSA), is based on mathematics that are computationally impossible to reverse by classical computers. Shor’s algorithm is designed, if it’s run on a quantum computer powerful enough, to be able to defeat that math.
Bitcoin’s security model ECDSA is the foundation of a scalable system. This is due to a mathematical one-way assumption. The process of multiplying a private-key by the point on the curve is simple, but reversing the operation to get the private key is not possible. It is called the Elliptic Curve Discrete Logarithm Problem.
There is no way for a classical computer to recognize if it has been updated. “divide” This operation. This operation’s only choice is brute-force, which involves guessing each possible key. It is estimated that there are 2,256 keys. This number is so large, it surpasses the total number of atoms known in the universe. Bitcoin can be protected from any classical supercomputer on Earth today and into the future.
It would calculate. Quantum computers would not guess.
Shor’s algorithm is a 1994 theoretical procedure. If the underlying structure is sufficiently robust, it can be used to determine whether the system will work. powerful quantum computerThe algorithm uses quantum superposition in order to uncover the hidden mathematical patterns, namely the period. The algorithm can reverse engineer a public key in hours or even days to determine the private key behind it.
A hacker would not have to compromise a server. The attacker could harvest all the P2PK keys that were exposed on the blockchain and feed them to a quantum computer, then wait until the private keys are returned. After that, they would sign a deal and transfer Satoshi’s 1 million bitcoins.
Did you Know? According to estimates, a computer with at least ten million transistors would be required to break the encryption of Bitcoin. 2,330 stable logical qubits. Experts believe that because current qubits can be noisy and error prone, a fault-tolerant device would require more than one million qubits to produce 2,330 stable qubits.
What is the closest we are to Q Day?
Rigetti Quantinuum, for example, are in a race to develop a quantum computing device that can be used to crack cryptography. This is reducing the time frame from decades down to just years.
“Q-Day” It is a hypothetical scenario when a quantum computing device can break existing encryption. It was thought to be a long-distance possibility for many years. “10-20-year” The timeline of the problem is rapidly accelerating.
Quantum error-correction is why 1,000,000 physical qubits are needed to produce 2,330 logical qubits. The qubits themselves are fragile. Qubits are fragile and noisy. They can be affected by even small vibrations or temperature fluctuations, and radiation. This could cause them to lose their quantum state and result in errors.
Stable logical qubits are required to perform a complex calculation such as breaking the ECDSA. For a logical bit, it may be necessary to combine tens or thousands of physical bits into an error-correcting algorithm. The system overhead is required to maintain stability.
The quantum race is accelerating rapidly.
-
Quantinuum and Rigetti, as well as tech giants like Google and IBM are publicly following aggressive quantum roadmaps.
-
Rigetti for instance, is still on schedule to have a 1000-plus qubit system in place by 2027.
-
These publicized achievements do not include classified research at the state level. First nation to achieve Q-Day would theoretically have the key to all global intelligence and financial data.
Defending against an attack requires that the defense is built and ready to deploy before it can happen.
The quantum attack on Bitcoin is a threat to millions
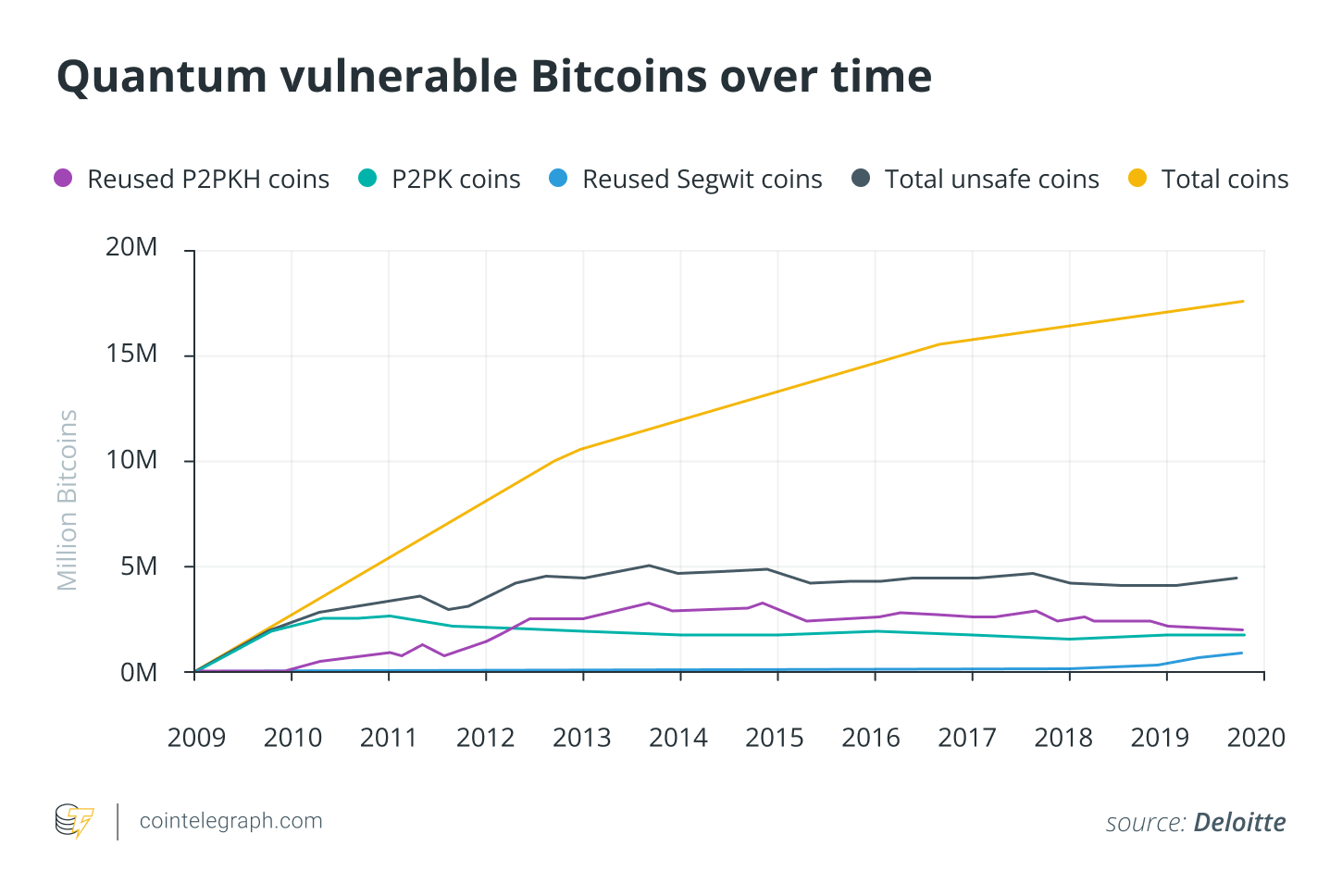
According to a report by the 2025 Human Rights Foundation, 6.51 Million BTC are in addresses that could be vulnerable, and 1.72million of them, including Satoshi, is considered unmovable.
Satoshi’s wallet may be the most valuable prize but isn’t the only one. A date in October 2025 report Human Rights Foundation has analyzed all of the blockchain to determine its quantum vulnerabilities.
These findings are shocking
-
Quantum attacks with a long range are capable of compromising 6.51 BTC.
-
Satoshi is estimated to have 1.1 Million BTC. Many of these are in P2PK address.
-
A further 4,49 million BTC are vulnerable, but can be protected by migration. This suggests that their owners may still have the ability to act.
Users made the critical error of reusing addresses. This 4,49,000,000 BTC is theirs. After spending money from the modern P2PKH address (which revealed the public key), users received funds to this same address. In the early 2010, this was a common practice. Reusing the same address permanently exposes their public key, making their modern wallet just as vulnerable to attack as Satoshi’s.
The simple act of moving Satoshi’s coins as proof that an attack was successful would be the case if a hostile actor reached Q-Day first. The act of moving Satoshi’s coins would serve as proof that the fundamental security of Bitcoin had been compromised. It could cause a market panic and a run on exchanges, along with an existential crisis in the crypto-ecosystem.
Did you Know? The most common tactics used by terrorists are: discussed It is a good idea to use a bilingual translator “harvest now, decrypt later.” Many malicious actors have already started recording data that is encrypted, like internet traffic or blockchain public keys. They plan to decrypt it in the future, once they get a quantum computing device.
Bitcoin’s quantum-safety protection
All of the tech industry is working towards new standards that are quantum resistant. Bitcoin would need to upgrade its network, or “fork”, in order to adopt a different algorithm.
The cryptographic community does not wait for it to happen. This is not the solution. post-quantum cryptography (PQC)A new generation of cryptographic algorithms based on more complicated mathematical problems, which are thought to provide security against quantum and classical computers.
Many PQC algorithms use structures like lattice cryptography instead of elliptic curvatures. This effort has been led by the US National Institute of Standards and Technology.
-
By August 2024 the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) will have published their first PQC finalized standards.
-
The key one for this discussion is ML-DSA (Module-Lattice-based Digital Signature Algorithm), part of the CRYSTALS-Dilithium standard.
-
It is now being used by other tech companies. OpenSSH 1.0 will have been adopted by late 2025. made Cloudflare has made a PQC algorithim its default and reported that the majority of their web traffic now is PQC protected.
Bitcoin’s path forward is almost certain to be implemented through a soft-fork, a system update that would affect the entire network. The upgrade will introduce quantum-resistant addresses, like the proposed “P2PQC” addresses. This would not require anyone to relocate. Users could instead voluntarily transfer funds to the new, secure addresses from old, insecure ones, like P2PKH and SegWit. It would follow a similar approach to the SegWit upgrades.
“This article is not financial advice.”
“Always do your own research before making any type of investment.”
“ItsDailyCrypto is not responsible for any activities you perform outside ItsDailyCrypto.”
Source: cointelegraph.com


