What is cryptocurrency money laundering?
The process of crypto money laundering is the concealment and disguising of illegally acquired funds through cryptocurrency transactions. The criminals might operate on chain but transfer funds to the blockchain for laundering.
In the past, money laundering was done by using couriers and informal networks like Hawala. Unfortunately, the rise in digital assets has led to bad actors exploiting them. blockchain technology Transfer large sums of money. As technology and regulation continue to evolve, the authorities are working hard to prevent and track cryptocurrency money-laundering.
Large sums of money can be moved more quickly by criminals thanks to the sophistication of technologies, such as cryptocurrency. The illicit activities in the cryptocurrency space have increased as well, due to the growth of adoption. By 2023. crypto wallets By 2022, the amount of money related to illegal activities will reach $31.5 billion.
Crypto money laundering: stages
A structured crypto-money laundering procedure is used to disguise the sources of illicit funds. To bypass anti-money laundering (AML), regulatory controls and oversight by criminals, they use complex methods. This process is divided into several phases:
- Step 1 — Gathering funds: First, you must collect funds that have been illegally obtained. This is often the result of organized crime and fraudulent activity. The funds must be transferred in a discreet manner to avoid being detected by regulators.
- Step 2 — Moving funds into the crypto ecosystem: Criminals move money into the system now by buying cryptocurrencies. It is common for criminals to make multiple purchases of cryptocurrencies. crypto exchangesThey are particularly weak in their AML compliance. They may also convert the funds to different digital assets, such as Ether.ETH), Polkadot (DOTUSDt or Tether (USDT).
- Step 3 — Juggling of funds: The criminals conceal the ownership of the funds at this point. In order to achieve this goal, criminals move their crypto-assets through different platforms and exchange one currency for another. Oft, money is transferred between accounts offshore and domestic to complicate the tracking process.
- Step 4 — Reintroducing cleaned money into the system: Final step is to reintroduce cleaned money in the economy. This can be done through a system of brokers and traders. The money is now invested in real estate, businesses or luxurious assets.
Did you Know? Taiwan’s Financial Supervisory Commission (FSC) has ordered that by 2025, all virtual asset service providers in Taiwan must follow new AML rules.
Criminals have a variety of methods to wash cryptocurrencies
Laundering digital assets obtained illegally is a method that criminals utilize. Criminals use different techniques to disguise the transactions trail, including non-compliant online exchanges and gambling platforms.
The following is a short description of some methods used by criminals.
Uncompliant central exchanges
The criminals are using centralized exchanges that do not comply with the law or peer-to-peer (P2P) platforms To convert cryptocurrency into cash. To hide the origins of cryptocurrency, it is converted to fiat through services such as mixers, bridges and decentralized finance protocols (DeFi).
CEXs still handled more than half of the funds despite their compliance. Nearly $23.8 billion worth of illicit cryptocurrency exchanged hands in 2022. This is a 68% increase from 2021.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs).
DEXs operate on a decentralizedPeer-to-peer means that transactions are made directly between users. smart contracts Instead of a CEX. These exchanges, currently unregulated and used by criminals for illicit purposes, are largely unregulated. swapping cryptocurrencies Making investigations more difficult.
Traditional dietary habits are not available. Know Your Customer (KYC) The AML procedure on most DEXs permits anonymous transactions.
Mixing services
Cryptocurrency mixersThey enhance anonymity when they pool digital assets coming from different sources, and then randomly distribute them to random addresses. Before the money is sent into legitimate channels, they hide their origins.
Tornado Cash was a popular example of criminals who used crypto mixers. It has been used to launder $7 billion in total from 2019 through 2022. Dutch authorities arrested the developer of this mixer.
Bridge protocols
Crosschain bridges, designed to transfer assets Money laundering is done by exploitation of the links between blockchains. These bridges are used by criminals to hide the source of funds, moving them between multiple blockchains. This makes it difficult for authorities to trace transactions.
Criminals can reduce their risk of being detected by converting assets that were previously on transparent networks into blockchains with enhanced privacy. Lack of regulatory oversight on different chains encourages illegal activity.
Online gambling platforms
Gambling platforms are frequently used by cryptocurrency money-launderers. Money launderers use gambling platforms to deposit money from anonymous or traceable sources. They then withdraw it directly, or they can collusively wager in order to hide the origin of funds. The process is effective. “legitimizes” The money.
In its report of September 2020, the Financial Action Task Force identified gaming services as money laundering risks, highlighting specifically suspicious funds flows into and out of these platforms, particularly when they are linked with known illicit sources.
Nested services
Nested services are services that operate in one or multiple exchanges and use addresses supplied by these exchanges. Some platforms are tolerant in their compliance standards when it comes to nested service, which creates opportunities for malicious actors.
The blockchain ledger makes it appear that transactions with nested service providers were made by exchanges, rather than the services themselves or the users who are behind them.
The Over-the Counter (OTC) Broker: A common service used for money laundering
OTC brokers have become the preferred nested services criminals use to launder money using crypto currency. They allow them conduct large transactions in cryptocurrencies securely, efficiently and with some anonymity.
The transactions may include different currencies, including BitcoinBTCETH) or convert crypto currencies to fiat currency, such as BTC into euros. OTC brokers are paid a commission to match buyers with sellers, but they don’t participate in negotiations. The broker supervises asset transfers between the parties once the conditions are agreed.
In order to combat cybercrime against North Korea, the US Government has taken tough action. Lazarus Group’s money laundering activities. The US Department of Justice sought to achieve this goal in August 2020. seize A $250 million exchange theft investigation revealed 280 addresses of cryptocurrency that were tied to 28.7 Million dollars in stolen funds.
In April 2023 the Office of Foreign Assets Control sanctioned two OTC traders and three other individuals for assisting Lazarus Group to launder illicit funds. This shows the continued dependence of the Lazarus Group on OTC brokers.
Did you Know? Microsoft Threat Intelligence identified Sapphire Sleet – a North Korean hacking collective – as being a major actor in corporate espionage, crypto theft, and cybercrime.
Explained: The changing landscape of cryptocurrency money laundering
Dual infrastructure is at the heart of the complex world of cryptocurrency money laundering. CEXs still remain the main conduits of illicit funds but there is a noticeable shift. In response to evolving criminal tactics, the use of gambling platforms and crosschain bridges is increasing. The analysis of crime patterns and deposit addresses reveals vulnerabilities.
Money laundering and crypto currency infrastructure
The crypto money-laundering infrastructure is broadly classified into wallets and intermediary services. Mixers, bridge protocols and other intermediary services are included in the category of intermediate services. decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols Other such services. Fiat off-ramping services Include any services that help convert cryptocurrency into fiat currencies.
Criminals can also make use of P2P exchanges and gambling services. crypto ATMs. Crypto criminals hide the source of money by using intermediary services that conceal the link in the blockchain between the address at the beginning and the address currently used.
The main channels for laundering crypto-currency
The ability of different financial services to fight money laundering varies. Centralized exchanges are able to control more transactions, and can freeze assets tied to illegal or suspicious sources. DeFi protocols are autonomous and don’t keep user money, so such interventions would be impractical.
Blockchain technology’s transparency allows analysts to follow funds as they pass through DeFi platform, something that is difficult when using centralized services. Between 2019 and 2023, centralized exchanges will continue to serve as the main destination for assets coming from illegal sources. A significant increase in ransomware proceeds being funneled to gambling platforms Ransomware wallets are increasingly sending money to bridges.
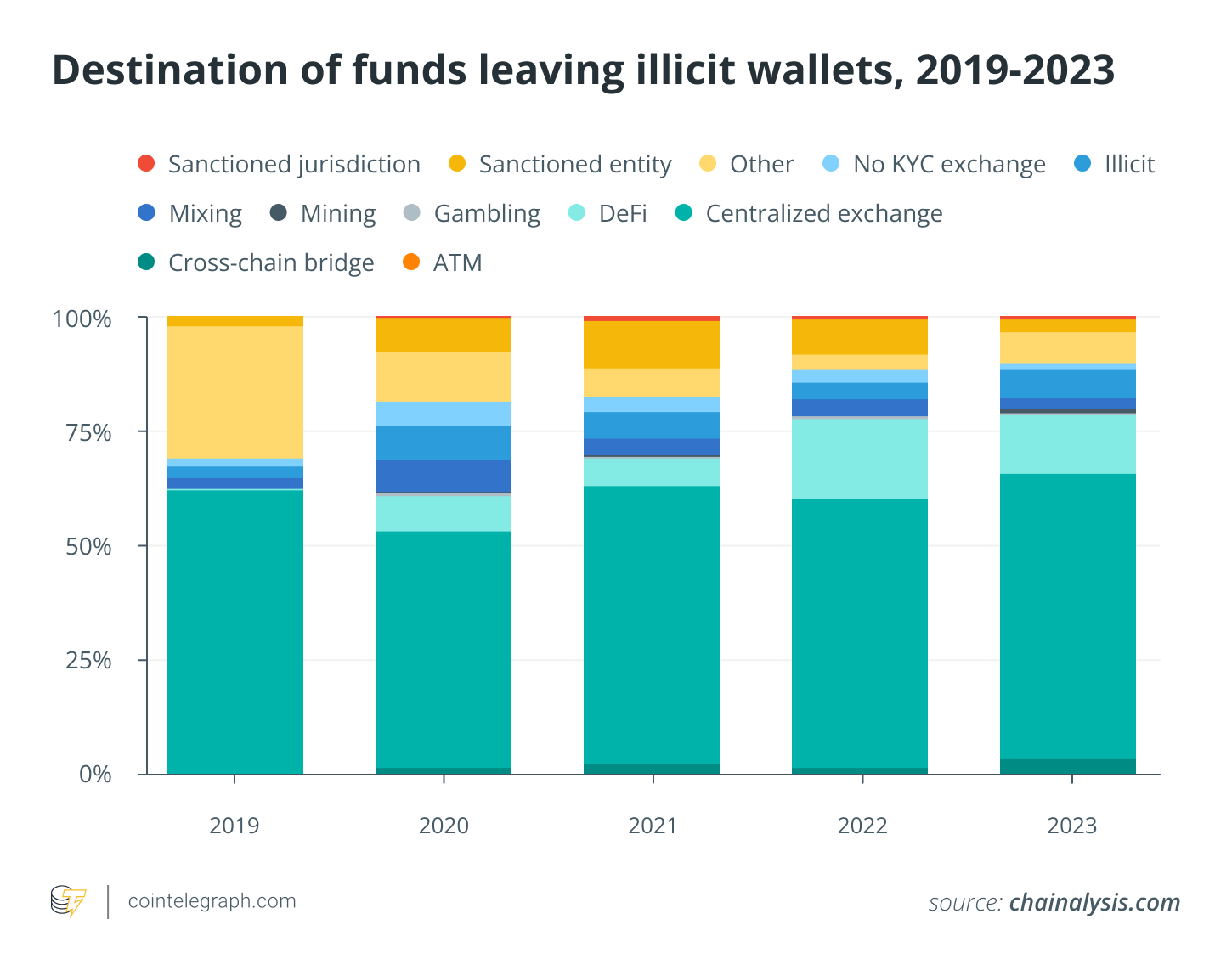
Tracing illegal funds using deposit addresses
The concentration of financial flows can be seen by the deposit addresses. These are similar to bank accounts, but on central platforms. A total of 109 addresses received more than $10 million each in illicit cryptos, together accounting for $3.4 Billion, by 2023. Only 40 of the addresses in 2022 exceeded $10 million, and accumulated a total just below $2 billion.
Money laundering concentrations also vary by criminal type. The centralization of ransomware and the vendors of illegal contents is high. 7 key deposit addresses received 51% of the funds exchanged from vendors of illegal content, whereas 9 addresses collected 50.3%.
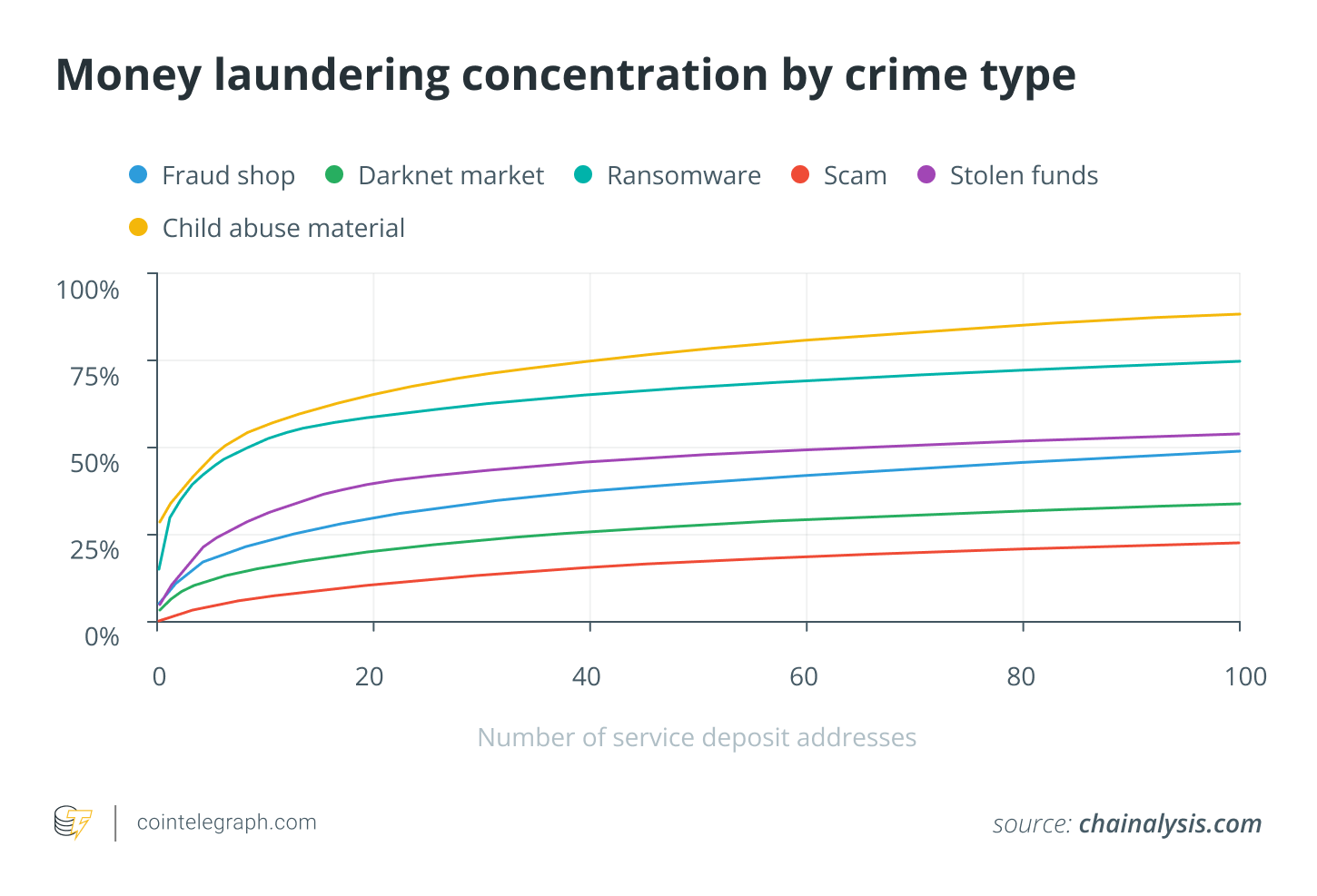
The criminals are shifting to mixing and cross-chaining services
Criminals who are more sophisticated use crosschain services and bridges to hide their transactions. Illicit crypto transactions through bridge protocol soared from $312.2 to $743,8 million dollars in 2023. The amount of funds being transferred from stolen asset addresses to bridges on cross-chain has increased dramatically.
Cybercriminal groups with sophisticated laundering techniques such as North Korean hacking group Lazarus Group use a variety of crypto services. They have modified their strategies over time in response to regulatory actions. In 2023, the Sinbad Mixer was shut down, and these groups began to use other mixing services such as YoMix which is available on the darknet.
Frameworks national and international for crypto AML
Worldwide, laws and guidelines have been implemented by governments to stop crypto money laundering. To ensure compliance, various national jurisdictions implemented regulatory frameworks.
United States
FinCEN, the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network in the US, regulates cryptocurrency asset providers. This is to help prevent money laundering. Under the Bank Secrecy Law, crypto exchanges are required to be registered with FinCEN. They also have to implement AML and counter-terrorist financing programs. The exchanges must keep proper records and report to the authorities.
Canada
Bill C-31, introduced in 2014 by Canada as the country’s first crypto-specific anti-money laundering legislation, was passed. The Proceeds of Crime Act, which prohibits money laundering and terrorist financing and covers transactions involving digital assets.
European Union
You can also find out more about the following: Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) Regulation The EU-wide crypto risk protection scheme aims to shield consumers from financial risks associated with cryptocurrencies. EU-wide Anti-Money Laundering Authority (AMLA) The Crypto Asset Service Providers (CASPs) have also been created. Crypto Asset Service Providers must share and collect transactional data in order to guarantee traceability. This is aligned with international standards.
Singapore
Singapore’s Payment Services Act governs services that use digital tokens for payments. For companies to be able to legally operate, they must comply with AML measures and perform due diligence on their customers.
Japan
Japan has strict regulations on cryptocurrency, including the Act on the Punishment of Organizational Crimes as well as the Act on the Prevention of Transfer of Criminal Proceeds.
The FATF is one of the organizations that countries have formed to collaborate on a global scale in order to prevent crypto-money laundering. The countries are also working to align regulatory frameworks, share information and strengthen AML frameworks.
In addition, tokens issuers are also crucial in the fight against illicit activities. Notably, stablecoins USDt) is a cryptocurrency that was created by Tether (USDTUSDCUSDC(), are equipped with mechanisms to prevent further abuse by blocking funds linked to criminal activity.
Crypto money laundering: How to avoid it
The crypto money laundering problem is increasing and forcing the authorities to use advanced Blockchain analytics in order to track illegal transactions. Law enforcement must therefore use sophisticated tools in order to identify suspicious activities and disrupt criminal networks.
As demonstrated by Silk Road where the analysis of blockchain helped to uncover criminal activities, law enforcement is becoming more proficient at tracking illicit transactions. Working with international organizations like the FATF, the European Commission and others, the authorities are able to assess jurisdictions at high risk and minimize threats against the financial system.
The crypto-service platforms should adhere to stringent KYC/AML protocols, in particular for those transactions that originate from high-risk regions. Platforms must regularly monitor transactions and look for any suspicious patterns. They should also work with the law enforcement agencies to quickly respond to possible laundering activities.
The users can also help by reporting any suspicious activity and avoiding dealing with companies operating in regions of high risk. Familiarizing yourself with secure wallet practices They are responsible for their own security. transactions are traceable By keeping records, you can avoid accidental participation in illegal activities. A strong level of cooperation between all parties will be key in preventing crypto money laundering.
“This article is not financial advice.”
“Always do your own research before making any type of investment.”
“ItsDailyCrypto is not responsible for any activities you perform outside ItsDailyCrypto.”
Source: cointelegraph.com


