Blockchain.com says that between June 15-24, Bitcoin’s hashrate experienced its steepest fall in the past three years.
Bitcoin’s hashrate decreased from nearly 943.6 billion terahashes per second (TH/s) on June 15 to 799.9 TH/s on June 24 — a decline of more than 15% and a level not seen since May.
A sharp fall in oil prices has fuelled speculation on possible environmental and geopolitical causes.
Many in the crypto community believe that Iran is the culprit behind this sudden drop in Bitcoin hashrate.

Related: 93% of all Bitcoin is already mined. Here’s what that means
Iran and its presumed connections
Iran has been known to conduct large-scale Bitcoin mines in the country. National Council of Resistance of Iran reported In late May, it was reported that local power failures were partly caused by large crypto mining operations, run or protected, in part, by Iranian state actors.
The connection between this and Iran is plausible. However, closer inspection raises questions about the theory. Iranian government imposed TechCrunch reports that the country will have a nearly total internet blackout for cyberattacks on 20 June.
It was also at the same time that global hashrate dropped from 884.6 millions TH/s to 865TH/s. This is a decrease of 2.2%.
On June 22, the US launched an airstrike on Iranian nuclear installations, according ReutersElectric grids were also affected. The global hashrate fell by 1% from 869.9 T/s to 860.9 T/s, on June 22, a drop of 1%.
Related: Bitcoin hashrate tops 1 Zetahash in historic first, trackers show
This connection is not strong
A little more than 3% of total hashrate decline coincided with the recent events in Iran. The hashrate also fell over 6.25 percent between June 15 and June 19 before the US bombed Iran or implemented the Internet blackout.
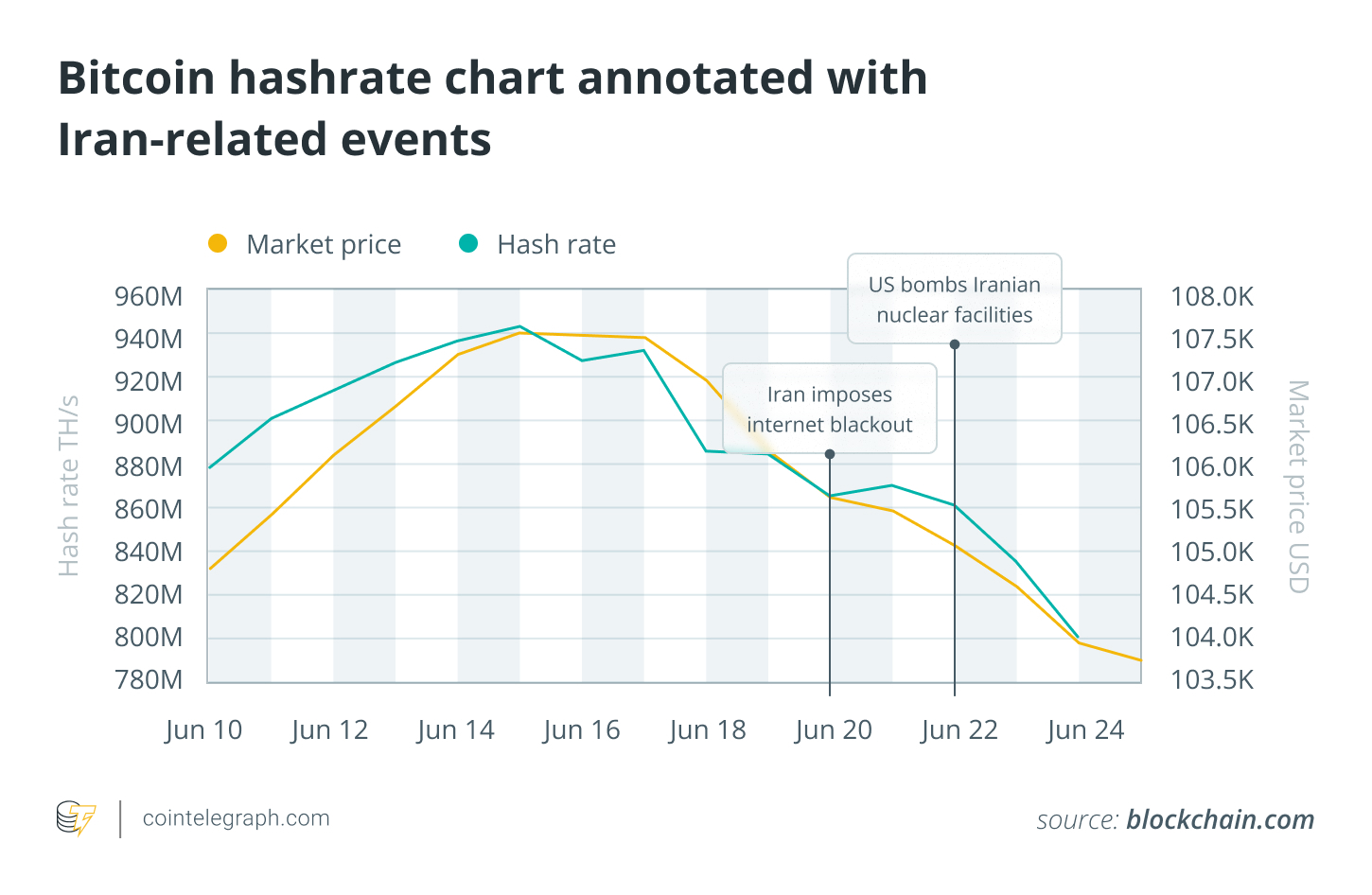
These data show that hashrate had already been in a downward trend before these events and this current fall is just a continuation. The events that are taking place in Iran may exacerbate this trend.
Another factor that is likely to play a part are the rising prices of electricity and ongoing heatwave In the US. Heatwaves can lead to lower efficiency in mining, and thus, the closure of low-profitable mining operations.
Heatwaves lead to increased power consumption and prices. This further reduces Bitcoin mining profitability. Con Edison of New York recently asked Customers are encouraged to conserve electricity during this heatwave. Power prices have risen in certain regions the most since January.
Bitcoin’s hashrate network isn’t directly measured. Instead, it is calculated using block time and the current mining difficulty.
The mining difficulty can be used to determine the average computing power required for a block. The hash rate calculation is inaccurate because computing power is averaged and there are significant variations in real mining based on pure luck.
The Iran Theory cannot be discounted for this reason. Market observers, however, suggest that a combination geopolitical and environmental pressures, as well as economic ones, are in play.
“This article is not financial advice.”
“Always do your own research before making any type of investment.”
“ItsDailyCrypto is not responsible for any activities you perform outside ItsDailyCrypto.”
Source: cointelegraph.com


